Hazard Codes & Pictograms
The Global Harmonised System
The Global Harmonised System (GHS) for Hazard Communication standardises the classification and labelling of chemicals. Its international implementation ensures that chemical hazard information remains consistent and is easily understood across different languages and regions. This system employs standardised hazard codes and pictograms to convey the severity and nature of chemical risks. Consequently, it facilitates a safer approach to chemical handling and use in workplaces worldwide.
OSHA Regulations on Hazard Pictograms
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires the use of specific hazard pictograms to protect employees from potential risks. The OSHA Hazard Communication Standard aligns with the GHS and requires employers to label chemicals with the appropriate pictograms that indicate hazard types such as flammability, toxicity or corrosivity. Compliance with OSHA standards ensures that employees are informed of chemical risks, thereby contributing to safer work environments.
Understanding Hazard Codes
Hazard codes are numerical or alphanumerical symbols that categorise the severity and type of chemical hazards. They provide a rapid reference for the potential risks of substances and assist in risk assessment and management. A code may indicate whether a chemical is flammable, irritating or harmful upon inhalation. When employees understand these codes, they can take appropriate safety precautions, such as using personal protective equipment or following designated handling procedures.
The Importance of Pictograms for Workplace Safety
Pictograms play a critical role in workplace safety by visually representing chemical hazards. They overcome language barriers so that every employee, irrespective of their first language, can recognise the risks. Their effective use contributes to accident prevention by providing immediate visual cues on necessary safety measures, for example, the need for ventilation, protective clothing or the prohibition of certain actions.
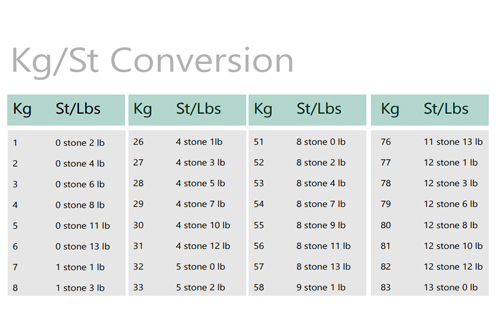
Table of Hazard Codes and Pictograms
Below is a table summarising the GHS hazard pictograms and corresponding codes:
|
Pictogram |
Code(s) |
Description |
|
Health Hazard |
H350, H360, H370, H372, H373 |
Indicates carcinogenic potential, reproductive toxicity or specific target organ toxicity. |
|
Flame |
H224, H226, H227, H228, H229 |
Identifies flammable liquids, solids, gases or self-heating substances. |
|
Exclamation Mark |
H332, H335, H336, H315, H317, H319 |
Indicates irritant properties, narcotic effects, respiratory irritation or irritation of the skin and eyes. |
|
Gas Cylinder |
H280 |
Denotes gas under pressure. If mishandled, it can cause explosion or rupture. |
|
Corrosion |
H314, H318, H332, H335 |
Indicates that the substance causes severe burns, eye damage or corrosive effects on materials. |
|
Explosive |
H201, H250, H260, H270 |
Denotes substances that are explosive, self-reactive or produce heat or explosive reactions with air or water. |
|
Skull and Crossbones |
H300, H301, H310, H330, H331 |
Indicates that the substance is fatal or toxic when swallowed, inhaled or absorbed. |
|
Environmental (Aquatic) |
H400, H410, H411, H412, H413 |
Indicates that the substance is extremely toxic, toxic or harmful to aquatic organisms, with long-lasting effects. |
This table provides a quick overview of the GHS hazard pictograms and their associated codes. Each pictogram corresponds to a specific hazard group relating to health, fire or environmental risks. For further information, please refer to Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Global Harmonised System (GHS)?
GHS is an international standard for the classification and labelling of chemicals. It ensures that hazard communication remains consistent worldwide.
How does OSHA enforce the use of hazard pictograms?
OSHA mandates that employers label chemicals with the appropriate GHS-compliant pictograms and provide safety training to employees.
Why are hazard codes important in the workplace?
They offer a rapid reference for identifying chemical hazards, assist in risk evaluation and ensure that appropriate safety measures are implemented.
Can pictograms be understood without language proficiency?
Yes, pictograms are designed to be universally recognisable. They facilitate effective hazard communication regardless of language.
How often should hazard labels be inspected or updated?
Labels should be inspected and updated when there is a change in the chemical’s hazard classification or the applicable safety standards.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us


 Chin Trento
Chin Trento