Medical Grade Titanium Materials - Indispensable To The Medical Industry
Titanium is a chemical element that is used in many applications in modern life. Its properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio, low density, high thermal resistance and corrosion resistance. It was first used in the aerospace industry for aircraft components. Today, the medical sector utilises titanium since it is non-toxic and bonds with human bone.
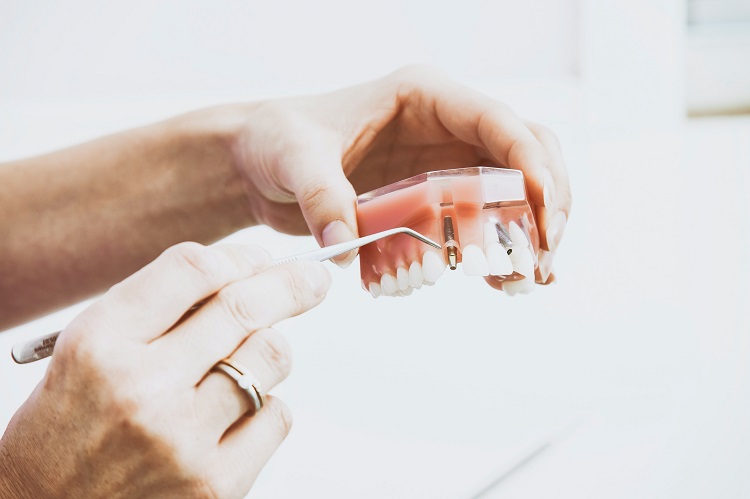
1. Types of Medical Titanium Alloys
Many titanium alloys exist with industrial applications; however, only Titanium 6AL4V and 6AL4V ELI are suitable for medical use. These alloys contain 6% aluminium and 4% vanadium. They are also known as Grade 5 and Grade 23 and demonstrate high biocompatibility with the human body. Several suppliers worldwide specialise in the distribution of titanium for medical applications.
In dentistry, Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-4V ELI are frequently used for implants. A titanium screw is inserted into the jaw and serves as a dental root. Time is allowed for the implant to bond with the bone. Once the bond is secure, an artificial tooth is attached.
2. Advantages of Medical Titanium Alloys
The alloys offer a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. They do not react with body fluids or acids, which increases their longevity. Titanium is used in various prosthetic applications, for example in the form of pins, plates, rods and cages that are implanted into the body.
Titanium is used in hip and knee replacement surgeries. It is also employed for the replacement of elbow and shoulder joints. Titanium pins are used for specific aesthetic purposes, such as in the support of false eyelashes. Additionally, titanium heart valves are manufactured for patients who require them.
3. Titanium Materials for Surgical Instruments
Titanium is harder than some steel grades and lighter than these materials. It is combined with other materials to produce surgical instruments that must be durable, light and corrosion resistant. Common titanium surgical instruments include retractors, forceps, scissors, suture instruments, needles and needle holders.
4. Titanium Materials for Dentistry
Titanium bonds with human bone. This property leads dental practitioners to use it exclusively for dental implants. In this procedure, titanium screws are placed in the jaw. As new cells adhere to the implant, a bond forms between the bone and the screw.
5. The Future of Titanium Materials for Medical Purposes
Demand for medical titanium alloys is expected to increase over the coming years. As the population ages, many will experience weakened bones and require hip and joint replacements. Consequently, titanium will remain the selected material for both medical and dental applications.
Read more: Applications of Titanium Materials in Medical Engineering
Conclusion
We appreciate your review of this article. We trust that it has enhanced your understanding of the titanium used in the medical industry. For further information on titanium products, please visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for additional details.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is an international supplier of titanium products. The company has over 20 years of experience in the manufacture and distribution of titanium alloys for medical applications. SAM meets the research and production requirements of its customers and remains a trusted partner in the industry.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us
 Chin Trento
Chin Trento

