Osmium: Element Properties And Uses
Description
Osmium (Os) is a dense, hard, bluish-white metal with the highest density of any element. It is used in alloys, electrical contacts, and fountain pen tips. It is highly corrosion-resistant but toxic in oxide form.
Introduction to the Element
Osmium is one of the least abundant elements in the Earth’s crust, known primarily for its exceptional density and distinct characteristics. Its occurrence in nature is limited, typically found in minute quantities within platinum ores. As a member of the platinum group metals, osmium has intrigued scientists and engineers due to its rarity and unusual behaviour.
Chemical Properties Description
Osmium is classified as a transition metal that exhibits several oxidation states, most commonly +3 and +4. Its chemical properties are marked by a notable resistance to corrosion when in its metallic form.
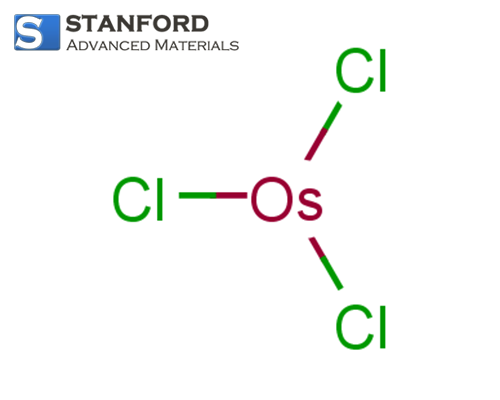
In compound form, osmium can form complex and sometimes hazardous compounds, such as osmium tetroxide—a substance known for its high reactivity and toxicity. Osmium tetroxide is used in specific staining procedures in microscopy, helping to reveal fine cellular details in biological samples.
The electron configuration of osmium, noted as [Xe]4f¹⁴ 5d⁶ 6s², contributes to its stability and low reactivity under ordinary conditions. Its chemical inertness is a key factor in the metal’s ability to withstand harsh environments.
Physical Properties
Osmium is renowned for being the densest naturally occurring element. Its physical characteristics include an extremely high density, impressive melting and boiling points, and a robust crystalline structure. The metal exhibits a metallic lustre with a slight bluish tint when polished, which adds to its distinctive appearance. These physical traits have positioned osmium as an important material in the field of materials science. The unique hexagonal close-packed crystal structure not only contributes to its density but also influences its mechanical properties, making it ideal for applications that demand high wear resistance and structural integrity.
|
Property |
Value |
Notes |
|
Atomic Number |
76 |
Fundamental property |
|
Atomic Weight |
190.23 g/mol |
Approximate average |
|
Density |
22.59 g/cm³ |
Highest density among elements |
|
Melting Point |
3033 °C |
Extremely high |
|
Boiling Point |
5027 °C |
Very high temperature |
|
Crystal Structure |
Hexagonal Close-Packed |
Unique crystalline form |
For more information, please check Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Common Uses
Osmium’s extraordinary properties have led to its use in several specialised applications.
It is commonly incorporated into alloys to improve hardness and wear resistance, which is particularly useful in the manufacturing of high-performance components. For example, osmium alloys are utilised in the tips of fountain pens, electrical contacts, and instrument pivots where durability is paramount.
In addition, osmium tetroxide, despite its toxicity, plays a crucial role in the preparation of biological specimens for electron microscopy by providing enhanced contrast.
Preparation Methods
The extraction and preparation of osmium are complex processes due to its low natural abundance and the chemical challenges associated with its compounds. Typically, osmium is obtained as a by-product during the mining of nickel, copper, and other platinum group metals. The separation process involves a series of chemical treatments, including oxidation and reduction reactions, to isolate osmium from other metals. Due to the hazardous nature of some osmium compounds, particularly osmium tetroxide, the preparation methods require stringent safety protocols and specialised equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is osmium?
Osmium is a rare, dense transition metal known for its outstanding physical and chemical properties, making it a unique subject in materials science.
Why is osmium considered the densest element?
Its exceptionally high atomic mass, combined with a compact atomic structure, gives osmium the highest density of all naturally occurring elements.
What are the main chemical compounds of osmium?
Osmium forms various compounds, most notably osmium tetroxide, which is widely used in staining techniques for electron microscopy despite its toxicity.
How are preparation methods for osmium performed?
Osmium is typically extracted as a by-product from platinum group metal ores using chemical reduction and oxidation processes, requiring specialised handling due to hazardous intermediates.
Which related industrial products commonly use osmium alloys?
Osmium alloys are used in high-performance applications such as fountain pen tips, electrical contacts, and precision instrument components where durability and resistance to wear are essential.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us



 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


