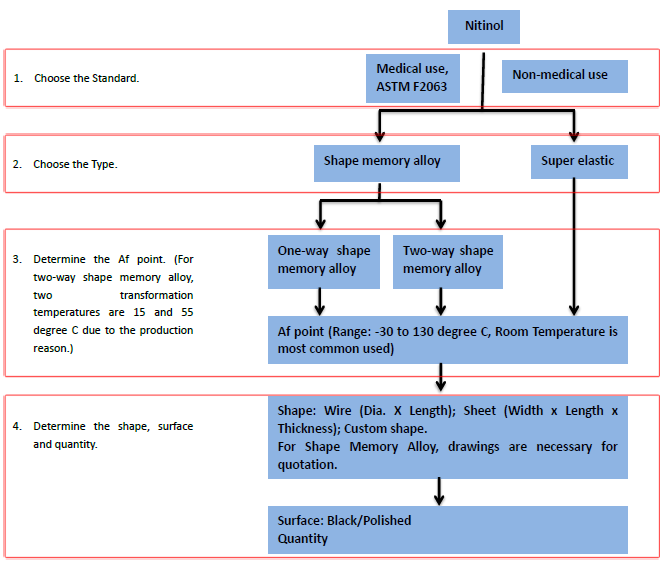
How To Finalize Your Demands For Nitinol
Nitinol (Nickel-Titanium)
Nitinol is a metal alloy consisting of nickel and titanium. Nitinol alloys exhibit two closely related and quantifiable properties:
Shape Memory Effect: The shape memory effect is the ability of Nitinol to deform at a specific temperature and to recover its original, undeformed shape when heated above its transformation temperature.
Superelasticity: Superelasticity occurs within a narrow temperature range slightly above the transformation temperature; consequently, heating is not required to restore the undeformed shape, and the material has an elasticity that is approximately 10–30 times that of conventional metals.
Af Point: The Af point is the final temperature at which the transformation from martensite to austenite concludes. Nitinol exhibits its superelastic properties or shape memory effect when heated above the Af point. (At which temperature does Nitinol become superelastic or recover its original shape?)
One-Way Shape Memory Alloy: The alloy can be deformed by an external force below the Af point and returns to its original shape when heated above the Af point.
Two-Way Shape Memory Alloy: The alloy adopts one shape at lower temperatures and a different shape at higher temperatures, with the change occurring automatically.
How can you fulfil your requirements?

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us
 Chin Trento
Chin Trento