Hyaluronic Acid For Osteoarthritis
Introduction
Osteoarthritis is a joint disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. One common site for osteoarthritis is the knee joint. Symptoms include pain, stiffness and restricted mobility. Hyaluronic acid is used to reduce pain and improve joint function. In this article, we explain the mechanism and efficacy of hyaluronic acid treatment for osteoarthritis. We hope you gain a better understanding of its properties and clinical applications.
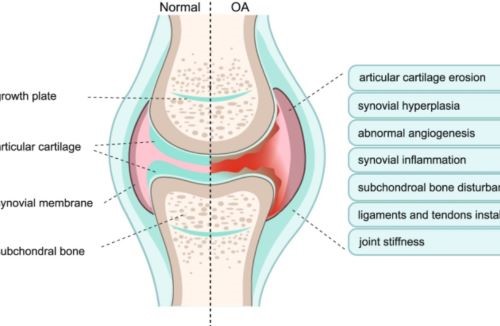
Figure 1. Osteoarthritis
Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis
Hyaluronic acid is a natural substance with hydrating and lubricating effects. It is present in the human body, for example in the umbilical cord, vitreous humour, choroid and synovial fluid. It attracts millions of water molecules, which can improve skin smoothness. HA may reduce friction and external pressure on joints. HA supplements and injections are used in osteoarthritis treatment. The high concentration of hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid lubricates and cushions the joints. In an osteoarthritic knee, HA injections replenish the reduced levels of hyaluronic acid. Joint pain, inflammation and cartilage damage are reduced as a result.
Read more: What does hyaluronic acid do for joints?
Mechanisms of Hyaluronic Acid in Osteoarthritis
The mechanisms of hyaluronic acid treatment are complex and involve multiple factors. The lubricant, anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective properties of HA contribute to its therapeutic effect.
Cushioning Effect
We now describe the specific mechanisms of HA treatment and the associated studies. One hypothesis proposes that hyaluronic acid functions as a cushion which protects joint surfaces against friction and damage. The large molecules generate a cushioning effect that reduces pressure on joint surfaces. This reduction in pressure leads to pain alleviation and improved joint function. In addition, HA injections may form a physical barrier that reduces friction between joint surfaces.
Anti-inflammatory Function
Another hypothesis proposes that HA injections have anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a key factor in the onset and progression of osteoarthritis. HA molecules may bind to receptors on immune cells. This binding inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines, thereby reducing joint inflammation and alleviating pain.
Chondroprotective Effect
Hyaluronic acid also protects cartilage. Chondrocytes produce and maintain joint cartilage. In osteoarthritis, chondrocytes may become injured or undergo apoptosis. This injury leads to cartilage loss and joint degradation. HA injections have been shown to stimulate the production of extracellular matrix molecules by chondrocytes. This stimulation may help repair and regenerate cartilage.
Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid in Osteoarthritis
Several clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of HA injections in treating knee and hip osteoarthritis.
- A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials showed that HA injections reduced pain and improved joint function compared to placebo. The effect lasted for up to 6 months after treatment. [1]
- Studies showed that hyaluronic acid reduced pain and may modify joint structure. Inflammation in the synovium decreased and chondrocyte density and viability improved. [2]
Conclusion
Hyaluronic acid treatment is a frequently used therapy in osteoarthritis management. Its mechanisms include lubricating, anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective actions. Several clinical studies have verified that HA injections reduce pain and improve joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Further research is required to fully elucidate the mechanisms and optimise the clinical application of HA treatment.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) has extensive experience in the manufacture and distribution of hyaluronic acid. On our website, HA is available in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, injectable and food-grade quality. Hyaluronic acid with high, medium and low molecular weights is also available. For further information, please visit our homepage.
References:
[1] Migliore A, Procopio S. Efficacy and Benefit of Hyaluronic Acid in Osteoarthritis. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2015 Jan-Apr;12(1):31–33. doi: 10.11138/ccmbm/2015.12.1.031. PMID: 26136793; PMCID: PMC4469223.
[2] Frizziero L, Govoni E, Bacchini P. Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Clinical and Morphological Study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998 Jul-Aug;16(4):441–449. PMID: 9706425.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators





 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


