Sodium Hyaluronate Products Of Different Technical Specifications: Molecular Weight And Viscosity
Introduction
Sodium hyaluronate (SH), the salt form of hyaluronic acid, is a naturally occurring polysaccharide. It is utilised in both cosmetic and medical industries because it may enhance skin moisture, skin texture and overall appearance. SH is available in several technical specifications, including different molecular weights and viscosities; these parameters affect its performance in various applications. This article examines the different types of SH products and their specific applications, thereby assisting research and industrial selection.
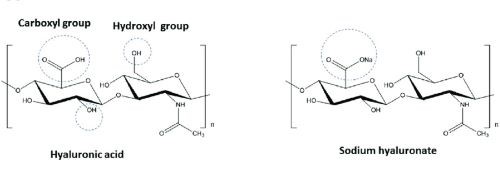
Figure 1. Chemical structure of HA and SH
Sodium Hyaluronate: Molecular Weight
The molecular weight of SH is an essential parameter that determines its physical and biological properties. Generally, a higher molecular weight results in increased viscosity and elasticity. Consequently, SH with a higher molecular weight is preferred for cosmetic applications, while SH with a lower molecular weight is used in medical applications, given that it is absorbed more efficiently.
- Low-molecular-weight SH (LMW-SH): LMW-SH has a molecular weight of less than 1 000 kDa and is commonly used in medical treatments such as joint injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis. It exhibits high bioavailability and may reduce inflammation and improve joint function.
- Medium-molecular-weight SH (MMW-SH): MMW-SH has a molecular weight between 1 000 and 1 500 kDa and is typically applied in cosmetic procedures, for example as a dermal filler and a skin moisturiser. It offers a moderate viscosity and elasticity that can be effective in reducing fine lines.
- High-molecular-weight SH (HMW-SH): HMW-SH has a molecular weight of more than 1 500 kDa and is equally used in cosmetic applications. Its high viscosity and elasticity are beneficial for sustaining skin volume and moisturisation over longer periods.
Further reading: High vs. Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid
Sodium Hyaluronate: Viscosity
The viscosity of SH is another critical parameter that influences its suitability for distinct applications. Highly viscous SH is employed in cosmetic products to provide a thick, gel-like consistency that fills wrinkles and adds volume. In contrast, low-viscosity SH is used in medical applications because it is easier to inject.
- Low-viscosity SH: Low-viscosity SH has a viscosity of less than 50 000 mPa·s and is typically formulated for joint injections and other medical devices. It features high bioavailability and can be rapidly absorbed, thereby reducing inflammation and improving joint performance.
- Medium-viscosity SH: Medium-viscosity SH has a viscosity ranging from 50 000 to 1 000 000 mPa·s and is used in the production of dermal fillers, moisturising creams and other cosmetic products. It provides a moderate consistency that fills wrinkles and adds volume to the skin.
- High-viscosity SH: High-viscosity SH has a viscosity greater than 1 000 000 mPa·s and is applied in cosmetic formulations. It offers a thick, gel-like consistency that may maintain skin volume and moisturisation for an extended period.
Further reading: Viscosity, Molecular Weight and Rheological Properties of HA
Conclusion
In summary, sodium hyaluronate products are available with various technical specifications, including different molecular weights and viscosities. The precise selection of an SH product based on its technical parameters is vital for achieving the desired performance while ensuring safety and efficacy. By selecting the appropriate SH formulation for a given application, healthcare providers and industry users may benefit from the functional properties of this polysaccharide.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a reliable supplier of sodium hyaluronate in various specifications. We provide sodium hyaluronates with high, medium and low molecular weights. Custom formulations are available. Please visit our website for further information.
Reference:
[1] Khaleghi, Maryam; Ahmadi, Ebrahim; Shahraki, Mahvash; Aliakbari, Farhang; Morshedi, Dina. (2020). Temperature-dependent formulation of a hyaluronic acid-polydimethylsiloxane hydrogel for biomedical applications. Heliyon, 6, e03494. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03494.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators





 Chin Trento
Chin Trento



