Specific Gravity: Liquids, Gases, And Solids
Below is a detailed compendium of measured specific gravities for various substances. The data are presented in tables and are provided for academic and industrial reference.
Specific Gravities of Liquids
|
Liquid Substances |
(°C) |
(SG) |
|
1-Propanol |
20 |
0.803 |
|
2-Propanol |
20 |
0.786 |
Specific Gravities of Gases
|
Gases |
|
|
Acetylene (Ethyne) |
0.899 |
|
Air |
1.000 |
|
Alcohol Vapour |
1.601 |
Specific Gravities of Solids
|
Solids and Metals |
Specific Gravity |
|
ABS, extrusion type |
1.05 |
|
Acrylic Glass |
1.19 |
|
3.4 |
|
|
Antimony |
6.69 |
|
Asphalt |
1.10 |
|
Cork |
0.25 |
|
Baryte |
4.50 |
|
Baryte |
3.62 |
|
Beryllium |
1.848 |
|
Bismuth |
9.79 |
|
Boron |
2.32 |
|
Cast Brass (rolled and cast) |
8.40 8.70 |
|
Red Brick |
1.75 |
|
Chamotte Brick |
2.40 |
Specific Gravity: FAQs
1. What is specific gravity?
Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference material (typically water) at specified conditions of temperature and pressure. This dimensionless quantity indicates the relative density of materials.
2. How is specific gravity calculated?
Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of the substance by the density of the reference material. The formula is provided below:
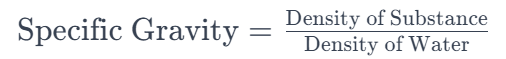
3. Why is specific gravity important?
Specific gravity provides a quantitative comparison of a material’s density against water. It assists in predicting whether a substance will float or sink when immersed and supports material selection in diverse scientific and engineering applications.
4. What does the value of specific gravity indicate?
l A value less than 1 indicates a density lower than water, implying buoyancy.
l A value greater than 1 indicates a density higher than water, leading to sinking in water.
5. Can specific gravity change?
Yes. Specific gravity may vary with alterations in temperature, pressure and physical state. Materials typically expand or contract with temperature, impacting their density and, consequently, their specific gravity.
6. How is specific gravity used across industries?
l In brewing, specific gravity measurements quantify sugar content before and after fermentation.
l In mining and metallurgy, it aids in assessing ore quality and mineral concentration.
l In construction, specific gravity helps evaluate the quality of concrete and aggregates.
7. How is specific gravity measured?
l Hydrometers measure the density of liquids to determine specific gravity.
l Pycnometers determine the volume of solids and liquids to calculate density and specific gravity.
l Archimedes’ principle is used for irregularly shaped solids to measure their displacement and density.
8. Are there limitations in using specific gravity?
Specific gravity is a useful quantitative parameter. However, it does not provide detailed compositional information and requires standard conditions for accurate comparison.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators




 Chin Trento
Chin Trento



