Common Types Of Chemical Identifiers
Chemical identifiers are distinct codes or symbols used to represent chemical compounds. They enable accurate differentiation and identification of specific substances in scientific research, industrial applications and regulatory frameworks.
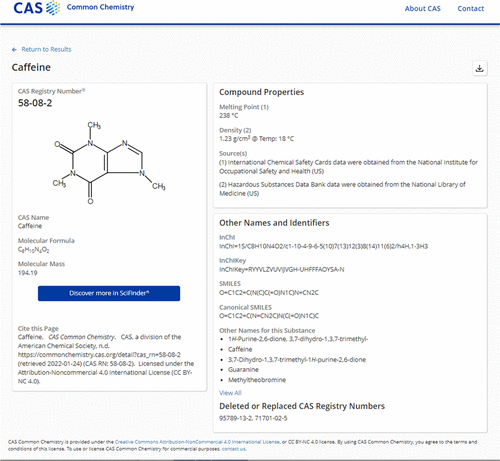
Figure 1. CAS Information on Caffeine [1]
Chemical Nomenclature:
Chemical names are assigned to compounds according to prescribed nomenclature rules, for instance IUPAC names or common names.
IUPAC Names:
The IUPAC system, which stands for International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, typically assigns names based on a compound’s molecular structure. It considers the types and arrangement of atoms. For example, Ethanol is the IUPAC name for the alcohol in beverages. 2-Methylpropan is the IUPAC name for a branched hydrocarbon with four carbon atoms.
IUPAC names for chemical compounds can be retrieved from online databases such as PubChem or ChemSpider. Authoritative chemistry textbooks, journals and mobile applications also provide access to IUPAC names.
Chemical Formulas:
Chemical formulas are symbolic representations that indicate the types and quantities of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2O represents water with two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
CAS Numbers:
CAS registry numbers (Chemical Abstracts Service) are unique numerical designations used to categorise chemical compounds. Each number comprises up to 10 digits separated by hyphens into three parts. The CAS registry contains records for substances such as elements, isotopes, metals, alloys and polymers.
Access to CAS registry numbers is available via sources and databases such as CAS SciFinder-n and CAS STNext. SAM and other chemical suppliers typically list CAS numbers alongside product details. CAS numbers are also provided on safety data sheets (SDS) and chemical labels.
InChI Codes:
InChI codes (International Chemical Identifier Codes) are unique textual representations of the structural information pertaining to chemical compounds. They serve as a standard method to represent molecular structure and bonding details in a format that is both human-readable and computer-interpretable.
InChI codes consist of a string that depicts connectivity, stereochemistry and isotopic details. They facilitate the exchange and retrieval of chemical data in databases and scientific publications, thereby ensuring accurate representation and identification of compounds.
SMILES:
SMILES stands for Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System. It is a string-based notation used to represent the structure of chemical compounds using ASCII characters. SMILES notations convey information regarding atom connectivity as well as spatial arrangement and bonding. This system provides a compact, human-readable representation of complex molecular structures.
Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII):
The Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII) is a non-proprietary, unique alphanumeric code assigned to substances in the FDA Substance Registration System. UNIIs facilitate accurate identification of substances in approval applications, databases and various health-related information systems. Each UNII serves as a unique identifier that enhances accuracy and efficiency in the classification and referencing of chemical ingredients in pharmaceuticals, food additives, cosmetics and other FDA-regulated products.
Reference:
[1] CAS Registry Number. (2023, 12/10/2023). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAS_Registry_Number

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators




 Chin Trento
Chin Trento



