6 Common Uses Of Titanium Dioxide Pigment
Introduction
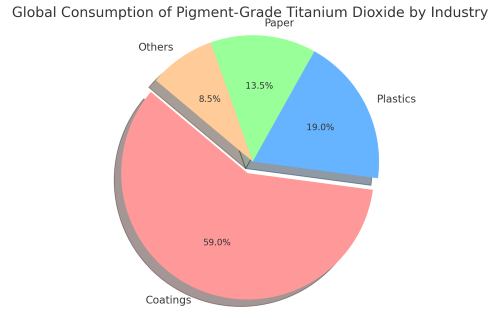
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) is a white pigment widely used in industrial processes. It is employed to manufacture white or light‐coloured products. This pigment enhances colour quality and opacity. Its applications cover several sectors. The primary sectors include coatings, plastics and paper.

1. Coatings
The coatings industry uses approximately 58 % to 60 % of the global TiO₂ pigment supply. This sector comprises paints, varnishes and various types of coatings. Products are prepared on solvent or water bases. Pulvrised and UV-cured coatings are manufactured using TiO₂.
Titanium dioxide is the principal pigment in coatings. It delivers high opacity and bright colours. It provides strong tinting strength and weather resistance. Consequently, coatings produced with TiO₂ show improved durability. The main applications are as follows:
- Vehicle coatings: They serve both aesthetic and protective functions.
- Architectural coatings: These include paints for buildings and other structures, with latex paints forming an important segment.
- Industrial coatings: These are applied to machines, equipment and other items.
- Marine coatings: They are used on ships and offshore structures to withstand harsh maritime conditions.
- Specialty coatings: Such coatings are used in the production of toys, household items and decorative objects.
Further reading: Everything You Need to Know About Titanium Oxides
2. Plastics
Plastics represent the second largest market, consuming roughly 18 % to 20 % of TiO₂ globally. The pigment improves whiteness, opacity and UV resistance in plastics. It enhances thermal and light stability. Consequently, degradation due to UV exposure is reduced. Its fine particle size and uniform dispersion improve light reflection and mechanical properties.
Common applications include:
- Packaging: Films, bottles and containers that require high opacity and visual appeal.
- Building materials: Pipes, claddings and fixtures benefit from enhanced durability.
- Consumer goods: Household items, toys and electronic casings are produced with improved quality.
- Automotive parts: Both internal and external plastic components employ TiO₂.
3. Paper
TiO₂ is the third major application sector, particularly in the United States where it is the second largest market. In paper manufacturing, TiO₂ increases brightness, opacity and printability. It is vital in producing high quality paper products such as:
- Fine papers: Used in books, magazines and premium printed materials.
- Thin papers: Employed in dictionaries and high‐quality magazines.
- Special papers: These include banknotes, computer papers and decorative varieties.
The use of TiO₂ in paper results in enhanced whiteness, increased gloss and smoother surfaces. This improves the overall quality and functionality of the paper.
4. Rubber
In the rubber industry, titanium dioxide functions as both a pigment and a filler. It improves durability, ageing resistance and mechanical strength. TiO₂ is particularly important in the following applications:
- Tires: It is used especially for the white sidewalls in car tires.
- Footwear: Sports shoes and rubber boots incorporate TiO₂.
- Rubber flooring: It provides consistent colour and structural strength.
- Various products: Items such as gloves, raincoats and sporting goods utilise TiO₂.
5. Chemical Fibres
TiO₂ is important in the chemical fibre sector, particularly for synthetic fibres. It is used as a de-dusting agent, reducing gloss by scattering light to produce a matte finish. Synthetic fibres, such as nylon, polyester and rayon, benefit from its high refractive index and optimised particle size distribution.
6. Printing Inks
Titanium dioxide is a key component in printing inks. It is used for its high opacity and tinting strength in applications including newspapers, books, magazines and packaging materials. TiO₂ contributes to consistent colouring and durability. Specific applications include:
- White and light-coloured inks: They achieve the required opacity and brightness.
- Special inks: These are used for printing on metal, ceramics and plastics.
Other Applications
Besides major industrial sectors, titanium dioxide is used in other fields:
|
Areas |
Benefits |
Applications |
|
Coatings |
High opacity, strong tinting and weather resistance |
Automotive, architecture, industrial, marine, specialty |
|
Plastics |
Improved whiteness, UV resistance and stability |
Packaging, construction, consumer goods, automotive |
|
Paper |
Enhanced brightness, opacity and printability |
Fine papers, thin papers, specialised papers |
|
Rubber |
Increased strength, durability and ageing resistance |
Tires, footwear, flooring, others |
|
Chemical Fibres |
Reduced gloss and improved matte finish |
Synthetic fibres (nylon, polyester, rayon) |
|
Printing Inks |
High opacity, consistent colouring and durability |
White, light colours, special inks |
Other applications include:
- Cosmetics: Used to achieve whiteness and opacity in products such as foundations and sunscreens.
- Pharmaceutical products: Utilised in tablet coatings and as a pigment in certain medications.
- Food additives: Employed as a colourant in specified food items.
- School supplies: Applied in art materials such as paints, coloured pencils and markers.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) provides a range of high quality titanium dioxide products at competitive prices. These products are available for various applications. The portfolio includes:
- Photocatalytic Nano-TiO₂: Used for environmental cleaning and self‐cleaning surfaces.
- Nano-TiO₂ for Lithium Batteries: Enhances performance and stability.
- Nano-TiO₂ for Ceramics: Improves strength and durability.
- Anatase and Rutile-TiO₂: Suitable for various industrial applications.
The products utilise the effective properties of TiO₂. They are required in sectors such as coatings, plastics, paper, rubber, chemical fibres and printing inks.
Conclusion
In summary, titanium dioxide pigments are essential in a number of industries. They improve colour, opacity and durability in a range of products. Given that quantitative data support its use, TiO₂ maintains its significance in global markets.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Chin Trento
Chin Trento



