Advantages Of Honeycomb Ceramic Filters
The ceramic honeycomb filter is used in metallurgy and foundry processes to filter molten metal. The filter comprises Mullite ceramic manufactured to precise standards with a dense, straight-cell structure. This configuration provides resistance to rapid temperature changes and a high sintering threshold. The straight channel design ensures a measured balance between flow rate and strength, thereby removing impurities and slag particles. Consequently, the mechanical properties, surface quality and cast product qualification rate are significantly improved. In this article, we examine the advantages of ceramic honeycomb filters.
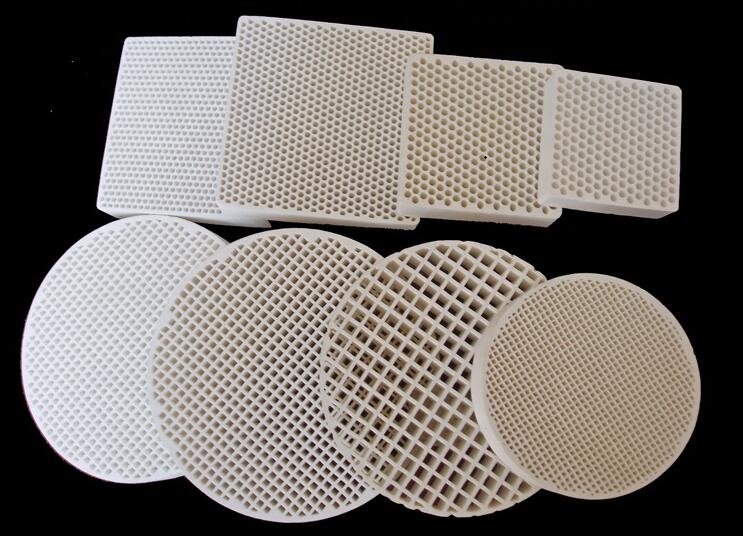
Benefits of Honeycomb Ceramic Filters
- Ceramic honeycomb filters demonstrate high temperature resistance, tolerance to rapid temperature fluctuations and are minimally affected by the flow of molten metal. No slag deposits or cracking occur during operation, thereby ensuring effective filtration of the molten metal.
- The ceramic honeycomb filter exhibits considerable strength at ambient temperature and is resistant to mechanical impacts. No cracking or damage is observed during use or transport, thereby facilitating both handling and operation.
- The ceramic honeycomb filter offers high filtering efficiency and outperforms fibre filters. Fibre filters exhibit lower performance in terms of filtering efficiency, reduction of turbulent molten metal flow and high-temperature stability. Consequently, foundry manufacturers frequently select the ceramic filter based on practicality, reliability, quality and cost efficiency to eliminate casting defects.
- The honeycomb-structured ceramic filter effectively reduces turbulence caused by casting, thereby ensuring a uniform fill and minimising surface defects in cast components.
- The ceramic honeycomb filter permits a high and stable molten metal throughput. In contrast, ceramic foam filters exhibit a gradual decrease in flow rate as captured inclusions accumulate. Even when numerous inclusions are present in the molten metal, normal operation does not lead to clogging of the filter.
- The ceramic honeycomb filter exhibits high chemical stability. It is unaffected by the acidity or alkalinity of the molten metal and does not alter its chemical composition.
- The honeycomb ceramic filter is produced to high dimensional accuracy and can be integrated into production lines where filters are placed automatically.
Conclusion
We appreciate your review of this article and trust that it has assisted in clarifying the advantages of ceramic honeycomb filters. Should you wish to learn more about ceramic honeycomb filters, please visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for further information.
As a recognised supplier in the field, Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) brings over two decades of experience in the manufacture and distribution of honeycomb ceramic filters. SAM provides its customers with ceramic honeycomb filters that meet the exacting specifications of both research and development and production environments. We are confident that SAM will serve as your preferred supplier and business partner for ceramic honeycomb filters.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators





 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


