Ultrasonic Testing
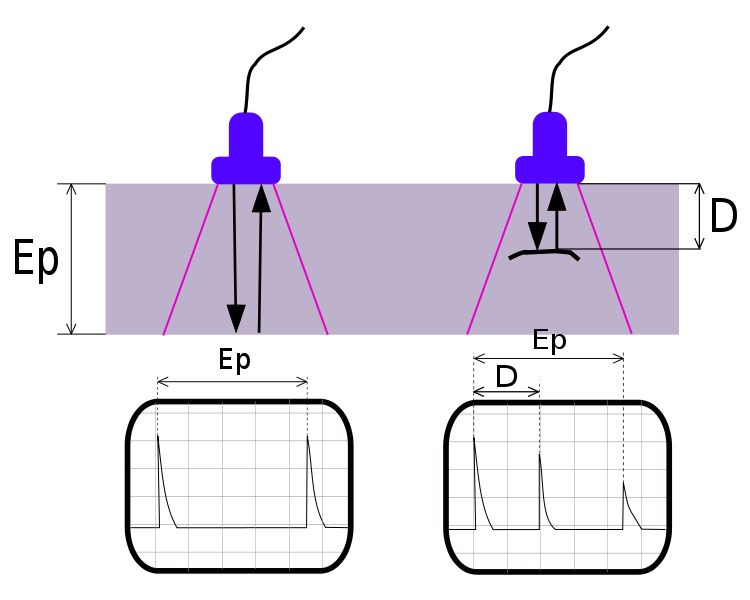
Ultrasonic testing (UT) comprises a set of non-destructive evaluation methods that rely on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse waves with centre frequencies of 0.1–15 MHz are transmitted into materials. Occasionally, frequencies up to 50 MHz are employed. A commonly used approach is ultrasonic thickness measurement, whereby the thickness of the object is measured to monitor, for example, the corrosion of pipelines.
Ultrasonic testing is routinely performed on steel and other metals and alloys. It is also applied to concrete, wood and composite materials, albeit with reduced resolution. The method finds use in a number of industrial sectors, including steel and aluminium construction, metallurgy, manufacturing, aerospace, automotive production and other transport sectors.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us
 Dr. Samuel R. Matthews
Dr. Samuel R. Matthews
