An Overview On Rare Earth Materials
Introduction
Rare Earth Elements play a central role in various industrial applications owing to their distinct physical and chemical properties. This article examines the importance of rare earth elements, their global distribution, and the specific applications in which their properties are used.
Rare Earth Elements and Global Occurrence
China, Russia, the United States, Australia, and India are the primary suppliers of rare earth reserves worldwide. Significant minerals such as bastnäsite, monazite, and ion-adsorbed rare earths are of strategic relevance for the global allocation of resources.
Understanding Rare Earth Elements
According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, rare earth elements consist of 15 lanthanides. Their atomic numbers range from 57 to 71. Scandium and Yttrium are also included because of their similar electronic structures and chemical properties.
Classification of Rare Earth Elements
The distinct physical and chemical differences between rare earth elements result in their categorisation into light and heavy groups. The first seven elements up to Gadolinium are designated as light rare earth elements, while subsequent elements, including Gadolinium, are classed as heavy rare earth elements. Yttrium, despite its lower atomic weight, is closely associated with the heavy rare earth elements because of its ionic radius.
Applications in Various Sectors
Rare earth elements are used in many industries. They contribute to the manufacture of fluorescent materials, components for metal hydride batteries, electric light sources, permanent magnets, and hydrogen storage solutions.
They also support the production of catalytic materials, precision ceramics, lasers, superconductors, magnetostrictive materials, magnetically cooled devices, magneto-optical storage systems, and optical fibre materials.
SAM's Expertise in the Provision of Rare Earth Elements
With over two decades of experience, Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a reliable supplier of rare earth metals and compounds. SAM offers a range of rare earth materials, excluding radioactive promethium, and maintains quality and competitive prices. Rare earth oxides are available in multiple stocks and can be delivered promptly upon order confirmation.
Illustrations
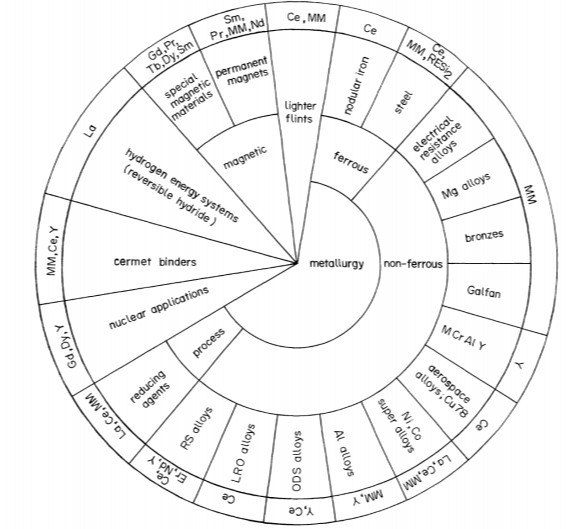
Application of Rare Earth Elements: metallurgical
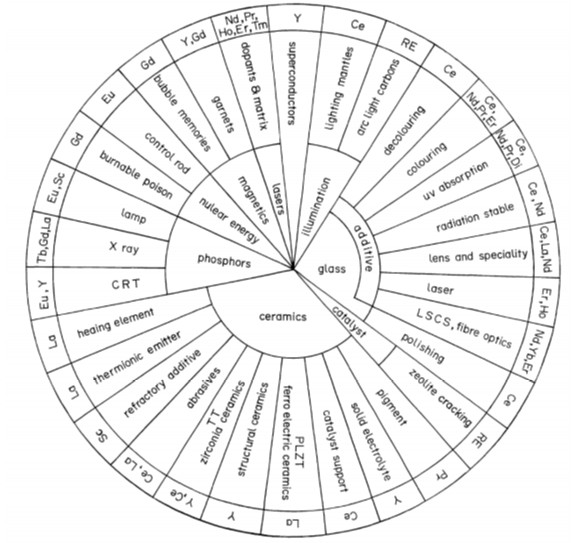
Applications of Rare Earth Elements: non-metallurgical
Conclusion
In summary, rare earth elements have become essential components of modern industrial practice. They increase the efficiency of electronic devices and support advanced metallurgical processes by utilising their specific properties. Stanford Advanced Materials ensures the supply of these critical materials, thereby supporting the continued development of several sectors.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us



 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


