Application Of 3D Printing Tantalum Powder In Biomedicine
Additive manufacturing attracted public attention approximately six or seven years ago as a new production method for the global manufacturing industry. The term "3D printing" was introduced.
The 3D printing of metals is used in various industrial applications. The process utilises digital simulation-based rapid prototyping. Metal, ceramic and plastic powders are applied in a layer-by-layer method. It is employed to produce plastic models and precision components. In certain cases, a complete car may be produced using this technique.
In biomedicine, 3D printing technology is used to produce artificial bones. Tantalum powder is a biocompatible material. It demonstrates high biological inertia and resistance to corrosion. This article examines the application of 3D printing using tantalum powder in biomedicine, for instance for hip joints.

Metalysis has produced a biologically inert tantalum lattice structure. The structure yields variable outcomes. It is engineered to match the mechanical stiffness of human bone. The lattice integrates with bone cells, thereby enabling tissue ingrowth. Stanford Materials provides ultrafine tantalum powder (D50=3 µm, D90<10 µm) for biological applications. When used in additive manufacturing and selective laser melting, this ultrafine tantalum powder maintains its structural integrity. The final surface may be further modified. The metallic properties remain stable.
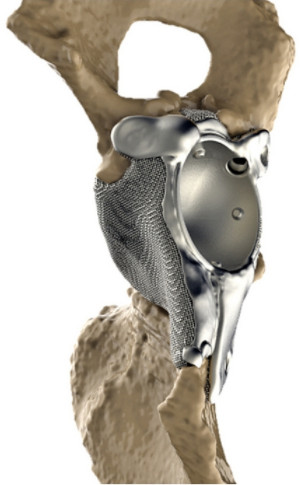
Tantalum powder is applied in the biological sector, especially in medicine. Metal 3D printing for hip joint replacement has been documented. By scanning the hip, customised metal replacements are manufactured using 3D printing. This method allows patients to receive bespoke hip joints. Previously, only standard sizes were available. In addition to hip joint implants, supportive lumbar cages for the spinal column are of interest to the industry.
Conclusion
We thank you for reading this article. We hope it has contributed to a better understanding of the application of 3D printing tantalum powder in biomedicine. If you wish to learn more about Ti products, please visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for further information.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a global supplier of tantalum powder. It has over twenty years of experience in producing and distributing tantalum products. Its products satisfy the research, development and manufacturing requirements of its clients. SAM is expected to fulfil the role of a supplier and business partner for tantalum.
Also read: Spherical Tantalum Powder for 3D Printing

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us



 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


