The Performance And Application Of Hafnium
Hafnium, chemical symbol Hf, atomic number 72, has a melting point of 2 233℃. It is a rare metal with a high melting point. In air, elemental Hafnium forms an oxide layer that provides substantial corrosion resistance and stable chemical properties. Hafnium metal powder is highly reactive and inflammable in air.
Hafnium and Zirconium exhibit a close association. No pure Hafnium mineral is found in nature. Zirconium minerals generally contain 1 % to 2 % Hafnium; some contain 5 % Hafnium. The extraction and processing of Hafnium is extremely complex. It is primarily sourced from Australia, South Africa, the United States, Brazil, India and other regions. Zircon sand serves as the raw material. Following extraction and separation, Hafnium oxide is obtained. Thereafter, chlorination, purification and reduction of Hafnium tetrachloride yield Hafnium sponge. Since Hafnium sponge is not malleable, it must be iodised and melted to form a Hafnium ingot. Subsequent forging, sandblasting, pickling and cold rolling produce strips, bars and other forms. Melting with other metals results in the formation of various Hafnium alloys.
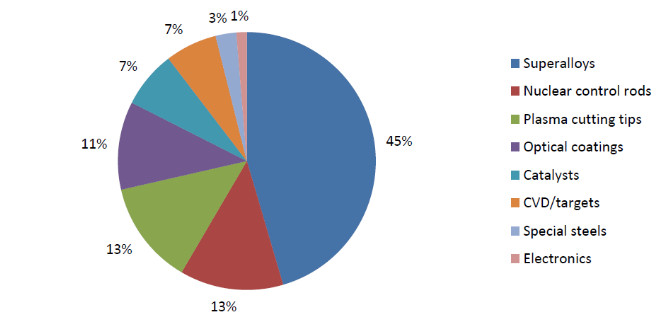
Owing to its favourable nuclear properties, Hafnium is widely utilised within the nuclear industry. It exhibits acceptable welding and machining characteristics, as well as high temperature and corrosion resistance. As a neutron absorber, it captures a wide range of thermal neutrons and is employed in the manufacture of control rods and protective devices for nuclear reactions. Additionally, Hafnium can emit electrons. It is used as a cathode in an X-ray tube and is a standard electronic material in the photovoltaic industry. Hafnium also functions as an alloying element offering high ductility, oxidation resistance and elevated temperature capacity. Niobium-Hafnium alloys containing approximately 10 % Hafnium are used in the aerospace industry. A Tantalum-Tungsten alloy with roughly 2 % Hafnium demonstrates high creep resistance and can be applied as a protective coating for spacecraft.
Further information: 4 Uses of Hafnium | The Applications of Hafnium and Hafnium Alloys

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us



 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


