Case Study: Elevating Aerospace Excellence With Titanium 6242 Alloy
Aerospace Industry Challenge
The aerospace industry must obtain a balance between structural integrity, fuel efficiency and overall weight. Conventional materials do not satisfy these requirements, which has led researchers to investigate advanced alloy options. In recent years, titanium alloys have assumed increased importance due to their specific properties.
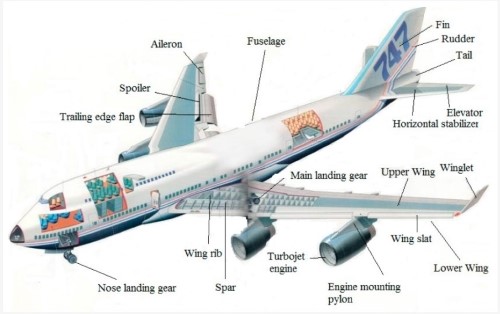
Figure 1. Aircraft Components
The Titanium 6242 Alloy for Aerospace Applications
Titan 6242 has been identified as a viable candidate for aerospace applications. Titanium 6242 (TI-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo-Si) is a medium-strength titanium alloy incorporating aluminium. It offers a notable strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. The alloy exhibits high strength, fatigue resistance and damage tolerance, thereby making it suitable for load-bearing structures in aircraft. Its corrosion resistance further ensures extended durability under harsh conditions.

Figure 2. Titanium 6242 Alloy
Owing to these attributes, Titan 6242 is applied in numerous aerospace components.
- Aircraft components: Titan 6242 is used in manufacturing critical components such as landing gear, wing structures, fuselage sections and engine parts. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance help maintain the structural integrity of the aircraft.
- Aerospace fasteners: The alloy is employed in the production of fasteners, including bolts, screws and nuts. These fasteners secure the assembly of components under extreme operating conditions.
- Engine parts: Titan 6242 is utilised in engine construction. It withstands elevated temperatures and resists corrosion. Consequently, its use contributes to improved engine efficiency and reduces fuel consumption and emissions.
- Aerospace propellers: The alloy is applied in the manufacture of propellers for manned and unmanned aerial vehicles. Its lightweight and high strength properties enhance propeller performance and fuel efficiency.
- Structural elements: Throughout the aircraft, Titan 6242 is used in items such as bulkheads, frames and beams. Its strength and corrosion resistance contribute to the overall integrity and durability of the structure.
- Aerospace springs: The alloy is used in manufacturing springs for aerospace systems. Its high strength facilitates precise energy storage and release in critical applications.
Further reading: Titanium in the Aerospace Industry
The Results
Overall, the use of the titanium alloy Titan 6242 in aerospace applications is significant. The combination of high strength, corrosion resistance and fatigue properties permits the development of solutions that maintain structural performance while reducing weight. Manufacturers continue to evaluate new material options; Titan 6242 remains a primary option for many aerospace applications.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) supplies titanium alloys with a defined purity and customisable material properties. Customised forms and component ratios are available. If interested, please submit an enquiry.
Reference:
[1] Gloria, A.; Montanari, R.; Richetta, M.; Varone, A. Alloys for Aeronautic Applications: State of the Art and Perspectives. Metals 2019, 9, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060662

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
.jpg)




 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


