Application Of Zirconium Compounds In Life
Zirconium Dioxide Ceramics in Daily Use
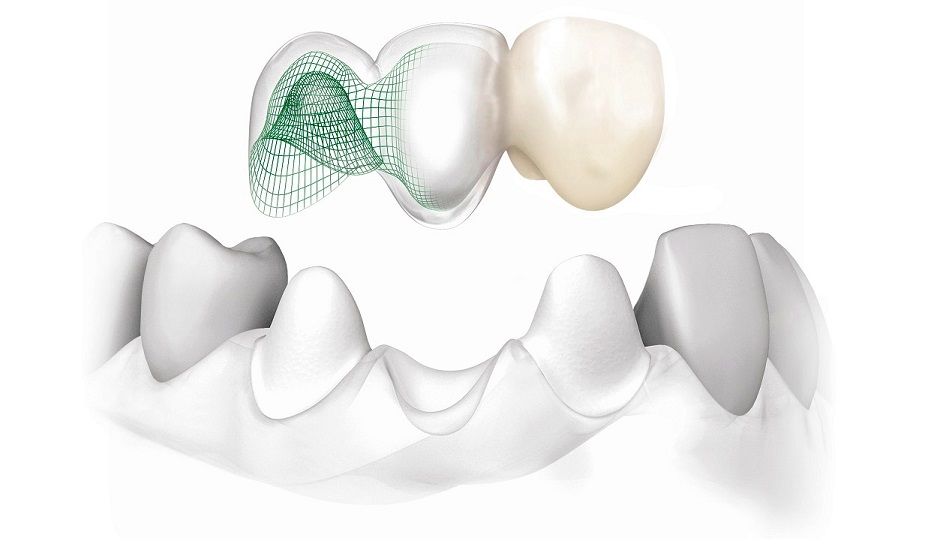
The most common form of zirconium compounds encountered in daily applications is the use of various ceramic materials composed of oxides. In dental practice, restorations made primarily from zirconium dioxide have gradually replaced metal-based and porcelain fixtures.
Because Zirconium is the principal material, public concerns have arisen regarding the possibility that all-ceramic prostheses may contain radioactive core constituents that could be detrimental to human health. This concern is particularly relevant for restorations placed directly in the oral cavity. Expert evaluations have demonstrated that zirconium dioxide materials maintain structural stability and do not undergo dissociation. Their compatibility with human oral tissues is supported by empirical studies. Consequently, zirconium dioxide restorations exhibit considerable wear resistance and acceptable aesthetic performance.

Zirconium Silicate in Daily Use
Ceramic tiles incorporating zirconium silicate are employed in a range of applications within the built environment. There have been reports indicating that ceramic tiles with a high degree of whiteness may exhibit levels of radioactive core elements exceeding established standards, thereby fostering a theory that such tiles are linked to cancer. Radioactive elements can induce cellular damage which may result in malignant tumours, such as leukaemia, lymphomas, skin cancer and other haematological cancers. However, no documented medical cases or recorded evidence exist to substantiate these claims. Given that, consumers are advised not to select ceramic tiles solely on the basis of their degree of whiteness.
Zircon Jewellery in Daily Use
Many individuals choose jewellery featuring faceted zircon. The colourless and transparent zircon, once cut and polished, provides a cost-effective option for jewellery manufacture. Its refractive index is approximately 2, and its dispersion measurements fall within the range documented for diamond. Under conditions of coloured illumination, zircon is used as a substitute for diamond. Its relatively low cost has positioned zircon as a common gemstone within the middle and lower price segments. The primary difference between diamond and zircon is that diamonds exhibit uniform reflective characteristics, whereas zircons display four bright and four darker facets. From the top, one can observe that the underside and ridge lines produce a distinct double shadow.

Conclusion
We appreciate your reading of this article and trust that it has contributed to a clearer understanding of the utilisation of zirconium compounds in daily applications. If you require further information on zirconium compounds, we recommend that you visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for additional details.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a multinational supplier of zirconium compounds with over two decades of experience in manufacturing and distributing zirconium products. We provide products that meet the defined research and production requirements of our clients. Consequently, SAM is anticipated to be your preferred supplier and business partner for zirconium.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us



 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


