The Use Of 3D Printing In The Automotive Industry
Introduction
The emergence of 3D printing has moved beyond the plastics sector and is now used within industries such as automotive manufacturing. Although common perceptions link 3D printing with plastic items, the automotive industry utilises methods such as selective laser sintering and selective electron beam melting to produce metal components. This article discusses the applications, advantages and limitations of employing 3D printing in the automotive sector, with particular reference to the work undertaken by Stanford Advanced Materials in advancing technical methods.
Further Reading: 3D Printing Powder: What It Is and How It Is Used?
Applications of 3D Printing in the Automotive Sector
- Vehicle Modelling: This method enables the production of full-scale models for accurate design evaluation.
- Design Verification: It confirms product reliability, structural integrity and strength during the design phase.
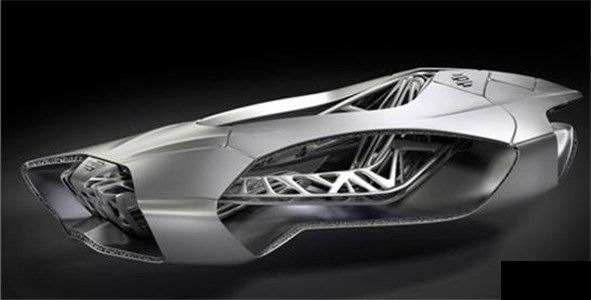
- Manufacture of Complex Components: It enables production of intricate parts that are expensive to produce using traditional techniques.
- Weight Reduction: It supports the manufacture of lightweight structural sections from both plastics and metals.
- Production Line Tools: It facilitates the fabrication of assembly components and precision measurement instruments for production lines.
Advantages of 3D Printing in the Automotive Industry
- Shortened Production Cycles: Recent trials indicate that processing time can be reduced by 37%, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing time-to-market.
- Enhanced Reliability: Established testing procedures ensure that product reliability is maintained throughout development.
- Cost Reduction: Expenses related to conventional manufacturing methods are minimised, notably by removing the need for specialised machining tools.
- Customised Production: It permits small-batch manufacturing and personalised production of automotive components.

Limitations of 3D Printing in the Automotive Sector
- Developmental Stage: 3D printing is still undergoing research and development and is not as mature as conventional production methods.
- Surface Quality: Additional processes such as polishing, colouring, electroplating and spray painting are required to achieve the desired finish.
- Material Limitations: The available range of materials remains restricted, which affects the entire production chain.
The Future of 3D Printing in the Automotive Industry
Given that the automotive industry is increasingly focused on lightweight construction, fuel efficiency and environmental impact, the utilisation of lightweight metals such as titanium alloys is expected to rise. The adoption of 3D printing powder technology thereby underlines the industry's commitment to measurable technical progress.
Conclusion
Although 3D printing in the automotive industry faces several challenges, its potential to modify manufacturing processes is evident. Stanford Advanced Materials plays a pivotal role in the controlled introduction of 3D printing techniques within the sector. As the industry develops, close collaboration between technical methods and material science is expected to further integrate 3D printing into regular automotive production.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us


 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


