The Role Of SOI In Automotive Systems
Introduction
In recent years, automotive engineering has advanced significantly. This change is driven by electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). Vehicles are becoming more complex. This increases the demand for semiconductor solutions that perform demanding computations while remaining energy-efficient and reliable.
One key innovation that meets this requirement is Silicon on Insulator (SOI) technology. SOI has proven essential for enhancing the performance and longevity of semiconductor devices. This is particularly important in automotive applications where safety, efficiency and lifespan are critical.
What is SOI Technology?
SOI is a semiconductor manufacturing technique in which a thin silicon layer is applied to an insulating substrate, usually silicon dioxide (SiO2). This structure improves the electrical performance of transistors by reducing parasitic capacitance. Consequently, processing speeds increase, current consumption decreases and thermal management improves. SOI-based devices are employed in consumer electronics, telecommunications and increasingly in automotive systems.

Further reading: Comparison between SOI and Silicon Wafers: Which is best for your semiconductor project?
Why SOI is Important for Automotive Systems
Modern vehicles incorporate numerous sensors, control units and communication systems. They require high computational power. These systems must operate reliably under extreme temperatures, vibration and electromagnetic interference. SOI technology offers several advantages for automotive applications.
1. Low Power Consumption
A major advantage of SOI technology is its ability to operate at lower power. Energy efficiency is critical in automotive systems, especially in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), where preserving battery life is a priority. SOI components reduce leakage current. Consequently, energy losses are minimised and overall efficiency improves. A study by GlobalFoundries reported that SOI-based chips use up to 30% less power than conventional silicon chips. This supports applications such as ADAS and infotainment systems.
2. Improved Thermal Performance
Automotive environments frequently experience high temperatures. The insulating layer in SOI structures reduces heat transfer between the silicon substrate and neighbouring components. Consequently, thermal management is enhanced. STMicroelectronics has demonstrated that SOI devices can operate at temperatures of up to 200 °C. This makes them suitable for powertrain control units and engine management systems. Improved thermal performance extends the lifespan of these chips and maintains consistent operation over time.
3. Enhanced Performance for ADAS and Autonomous Driving
ADAS and autonomous driving systems process large volumes of data from sensors, cameras and radar. They require high-speed processing and real-time data analysis in order to perform functions such as lane keeping, automatic emergency braking and adaptive cruise control. A study by the French research institute Leti indicated that SOI technology provides processing speeds that are 30% higher than those of conventional silicon components for ADAS systems. SOI-based chips also operate efficiently, which supports their integration into ADAS modules.
4. Excellent Signal Integrity and Noise Immunity
Automotive environments are often affected by electromagnetic interference (EMI) because several electronic systems operate concurrently. SOI technology provides excellent signal integrity and reduces the susceptibility to such interference. The insulating layer in SOI substrates shields transistors from disturbances. Consequently, electronic systems in vehicles operate reliably even in the presence of EMI.
SOI in Key Automotive Applications
As the automotive sector adopts next-generation technologies, SOI is used in various critical systems.
1. ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems)
ADAS functions such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, blind spot detection and automatic emergency braking depend on rapid and energy-efficient sensor data processing. SOI technology is implemented in the processors and control units that support these ADAS functions and provide the necessary real-time computational power.
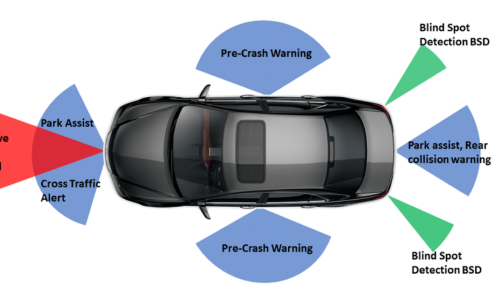 [1]
[1]
In 2020, the S32 microcontroller family was introduced using SOI technology. It reduced power consumption by 50% while maintaining high processing performance. This capability allows automotive manufacturers to incorporate advanced ADAS functions without compromising energy efficiency.
2. Powertrain and Battery Management
SOI technology is increasingly used in powertrain control units that optimise engine performance, reduce emissions and enhance fuel efficiency. In electric vehicles, SOI-based chips are also utilised in battery management systems (BMS) to monitor and control charging and discharging. For example, one SOI-based battery management system extended battery life by 15% owing to its energy-efficient operation and improved thermal handling. These systems operate efficiently to extend battery lifespan and optimise energy consumption.
3. Infotainment Systems
Modern infotainment systems offer functions such as GPS navigation, multimedia playback and wireless communication. They demand high processing performance combined with low power consumption. SOI technology enables the development of processors that manage complex tasks without excessive heat generation or power usage.
4. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
V2X communication enables vehicles to exchange information with other vehicles, infrastructure and pedestrians. This communication is critical for connected and autonomous vehicles given that it helps reduce accidents and improve traffic flow. SOI technology delivers the processing performance required for V2X systems, thereby offering low latency and high data throughput.
The Impact of SOI on Vehicle Safety and Reliability
Safety and reliability are critical in automotive engineering. SOI technology plays a central role in addressing these issues. Improved thermal performance and reduced power consumption decrease the risk of overheating and excessive power draw. Additionally, the improved noise immunity and signal integrity of SOI-based chips ensure reliable operation under electromagnetic interference. For safety-critical applications such as ADAS, reliability is paramount. A study reported that SOI-based sensors in ADAS systems reduced system failures by 25%. This makes them a preferred choice for manufacturers concerned with safety.
The Future of SOI in Automotive Systems
The shift towards fully autonomous vehicles and more advanced electric vehicles will increase the demand for high-performance, energy-efficient semiconductor solutions. SOI technology, with its advantages in energy efficiency, thermal management and signal integrity, is well placed to meet these requirements. Its applications are expected to expand to include advanced infotainment, V2X communication and other emerging automotive technologies.
Conclusion
In summary, Silicon on Insulator (SOI) technology is proving effective in the automotive sector. It provides the performance, low power consumption and reliable operation needed for systems under harsh conditions. As vehicles become more automated and intelligent, SOI continues to support technological advancements and maintain safety and efficiency in modern automotive systems. Further information about SOI is available at Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Reference:
[1] Chipengo, Ushemadzoro. (2018). Full Physics Simulation Study of Guardrail Radar-Returns for 77 GHz Automotive Radar Systems. IEEE Access. PP. 1-1. 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2881101.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Chin Trento
Chin Trento


